From its Origins to the Present Day
The registration card, or certificate of registration, is an essential administrative document for any vehicle owner in Belgium. This small piece of paper (initially) pink has undergone significant evolution since its inception, reflecting the transformations in society and the automotive sector.
The first vehicle registrations in Belgium date back to the late 19th century. At that time, registration was more localized, and license plates were often issued by local municipalities. If registration cards existed, they were simple documents with little standardization.
Throughout the 20th century, the Belgian registration system was gradually standardized. License plates adopted a more uniform format, and registration numbers were issued in a more systematic manner. The registration card itself adopted a standardized format, initially pink, and began to include essential information about the vehicle and its owner.
The Evolution of Colors and Visual Design
The visual design of the Belgian registration card has evolved over the years, depending on reforms and security needs.
- Pink: for many years, the Belgian registration card was recognized by its pink color. This format was used for several decades until around 2010.

- Sandy Yellow: in the 2010s, to improve security and combat fraud, the color of the registration card was changed to sandy yellow, with a front and back in different colors (blue and yellow). This new version also introduced new security features, such as watermarks, micro-letters, and holograms.

- Current Version: the Belgian registration card has undergone further changes, but the sandy yellow color remains the standard. The format and security features have been slightly adjusted, but the goal remains the same: to ensure the authenticity of the document and facilitate inspections.

Important: the visual design of the registration card may vary slightly depending on the vehicle’s registration date. Cars registered before the 2006-2010 reforms will retain the pink registration card, while vehicles registered afterward will have a sandy yellow card. With the advent of the digital age, the registration card has also undergone a transformation. Vehicle information is now stored in computerized databases, simplifying administrative procedures and enhancing security.
Recent Developments
In recent years, new features have been added to the Belgian registration card. For example, it is now possible to view your registration certificate online via the DIV (Vehicle Registration Authority) portal.
What is the Purpose of the Registration Card?
The registration card serves several essential functions:
- Vehicle identification: it carries a unique registration number that allows precise identification of the vehicle.
- Owner identification: the registration card indicates the name and address of the vehicle owner.
- Technical data: it contains technical information about the vehicle, such as the make, model, power, etc.
- Transaction: the registration card is required when selling a vehicle. It must be handed over to the buyer during the transaction.
In Practice
Here is an overview of the data that can be found on your registration card:
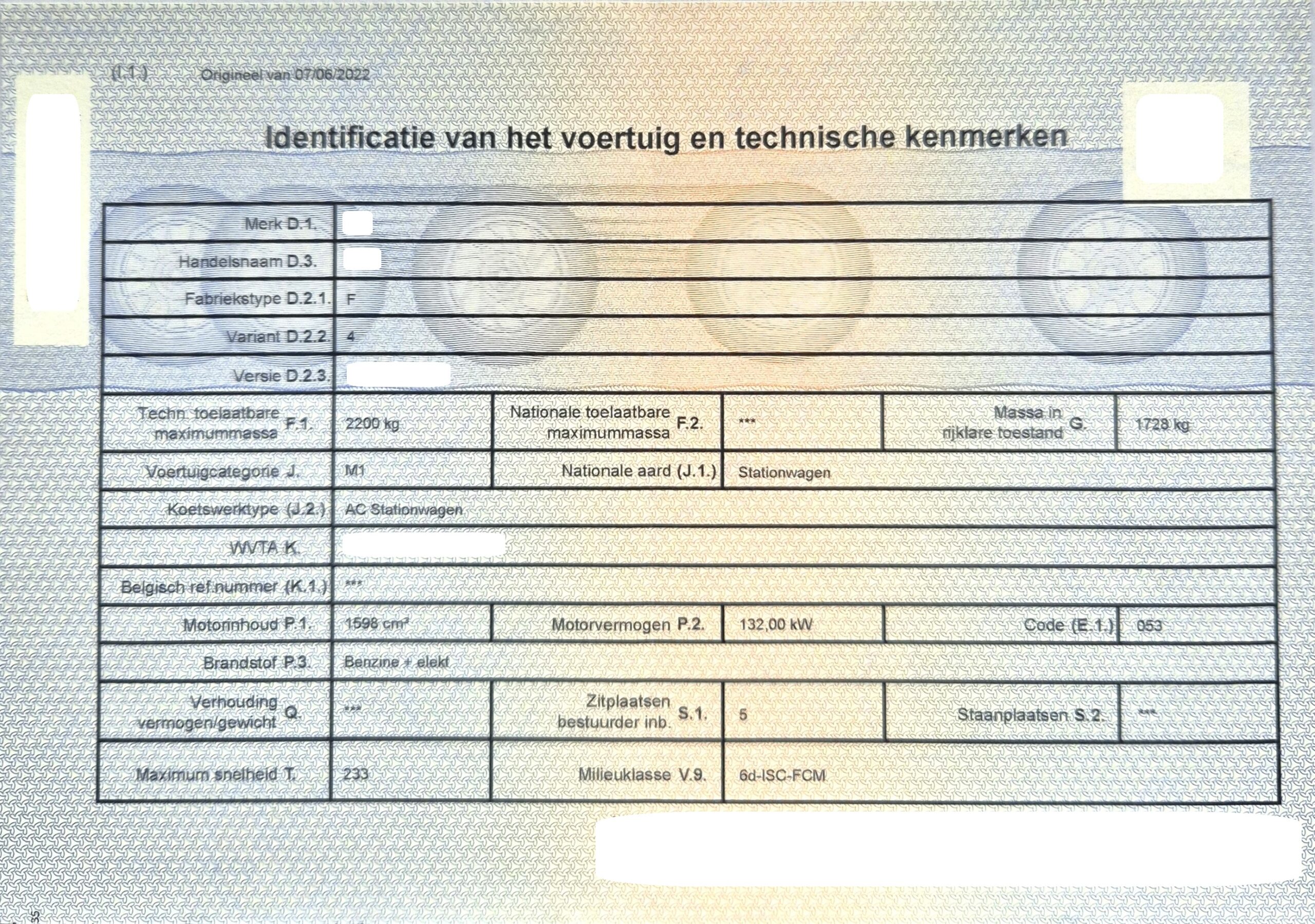
Vehicle Registration
A: The registration number specific to this car;
B: The date of the vehicle’s first registration;
I: The date when the current registration certificate was issued.
E: Vehicle Identification Number (V.I.N.): the VIN or chassis number is a unique code consisting of 17 characters. It allows exclusive identification of the vehicle and provides information about its history, previous owners, repairs, etc. You can find it directly on your car, with its location varying depending on the make and model. During a technical inspection, this number is used to verify with the registration certificate that it is indeed the correct car.
H: Blank, as it relates to the validity period of the registration certificate, which is unlimited.
Vehicle Owner Information
C.1: Name, first name, and address of the owner;
C.4a: Indicates that the individual listed in C.1 is the vehicle holder;
C.4.1: Lists the co-owners who can also use the vehicle;
C.3: The address associated with the registered vehicle, where you can receive mail related to your car, such as fines.
General Vehicle Information
D.1: The brand of your car;
D.3: The model of your car.
D.2 (2.2 & 2.3): Version, type, and variant of your car in a code;
D.2.1: The National Vehicle Identification Code (CNIT);
Vehicle Maximum Weights
F.1: The total (allowed) weight (in kg) of the vehicle;
F.2: The maximum authorized weight for your car only in the state of registration;
G: The weight of your car in its current state, including the driver.
Secondary Registration Information
J: Vehicle category;
J.1: National classification (distinguishing between private and commercial vehicles);
J.2: Vehicle code at the European level (bodywork);
K: Type approval number for imported vehicles.
P.1: Engine displacement (in cm3);
P.2: Maximum net power (in kW);
P.3: Fuel type;
P.6: Number of “fiscal horsepower” (national administrative power rating);
Q: Power-to-weight ratio in kW/kg. This only applies to motorcycles.
S.1: Maximum number of seats, including the driver’s seat;
S.2: Maximum number of standing passengers (applies to public transport vehicles);
T: Maximum speed of the vehicle;
V.9: Environmental class.
The Belgian registration card has come a long way since its origins. It has become an essential document in the automotive world, reflecting the evolution of society and technology. If you have any questions about your documents or vehicle insurances, feel free to contact us.






